What is the Waste Hierarchy?

Join us as we explore the eighth wonder of the modern world… the Great Pyramid of the Waste Management Hierarchy.
With the healthcare industry now on the route to Net Zero, finding more sustainable ways of managing waste is becoming increasingly important. In this blog, we’ll examine the fundamentals of the waste hierarchy, how it works, and why it’s an important tool for healthcare facilities to use to prioritise waste management methods that minimise environmental impact.
We’ll also explore some helpful steps for implementing the waste hierarchy that can be used for healthcare facilities of any size.
TOPICS WE WILL COVER:
1 / What Is the Waste Hierarchy?
2 / Why Is Prevention the Top Priority of the Waste Hierarchy?
3 / How Does the Waste Hierarchy Work?
4 / Why Is the Waste Management Hierarchy Important in Healthcare?
5 / Regulatory Compliance in Healthcare Waste Management
6 / Legal Context in Healthcare Waste Management
7 / Steps for Implementing the Waste Hierarchy
8 / Do You Need Guidance on Your Waste Management Strategy?
What Is the Waste Hierarchy?
The waste hierarchy is a framework tool that ranks waste management methods in order from the most to least favourable in terms of environmental impact, helping you to prioritise and manage your waste production in the most effective way. This version of the waste hierarchy is aligned with the newly updated Health Technical Memorandum (HTM) 07-01 and NHS Clinical Waste Strategy.
The Waste Hierarchy Pyramid
The inverted waste hierarchy pyramid graphic below shows the different steps that should be taken to manage healthcare waste with step one being the optimal solution and step seven being the last resort.
1. Prevention: Reducing the amount of waste generated by limiting the demand for products and material resources.
2. Correctly Segregate: Ensuring that generated waste is correctly segregated into the appropriate waste streams helps to maximise opportunities for reuse, recycling, and recovery.
3. Recirculate/Re-use: Recirculating and reusing products instead of disposing of them after a single use where suitable when waste cannot be prevented.
4. Recycle: Transforming waste materials into a new substance or product. Of course, this is a last resort for recovering material, exempting non-recyclable waste, because it usually entails using resources or energy to generate a new product.
5. Generate for Energy Sources: Using waste to generate energy and recover other resources such as water, heat, material, and nutrients.
6. Disposal: Sending waste to high-temperature incinerators or alternative treatment facilities.
7. Landfill: Transporting waste to landfill sites secures waste in a single location, but there’s a limited capacity. It also contributes to harmful greenhouse gas emissions (GHG). 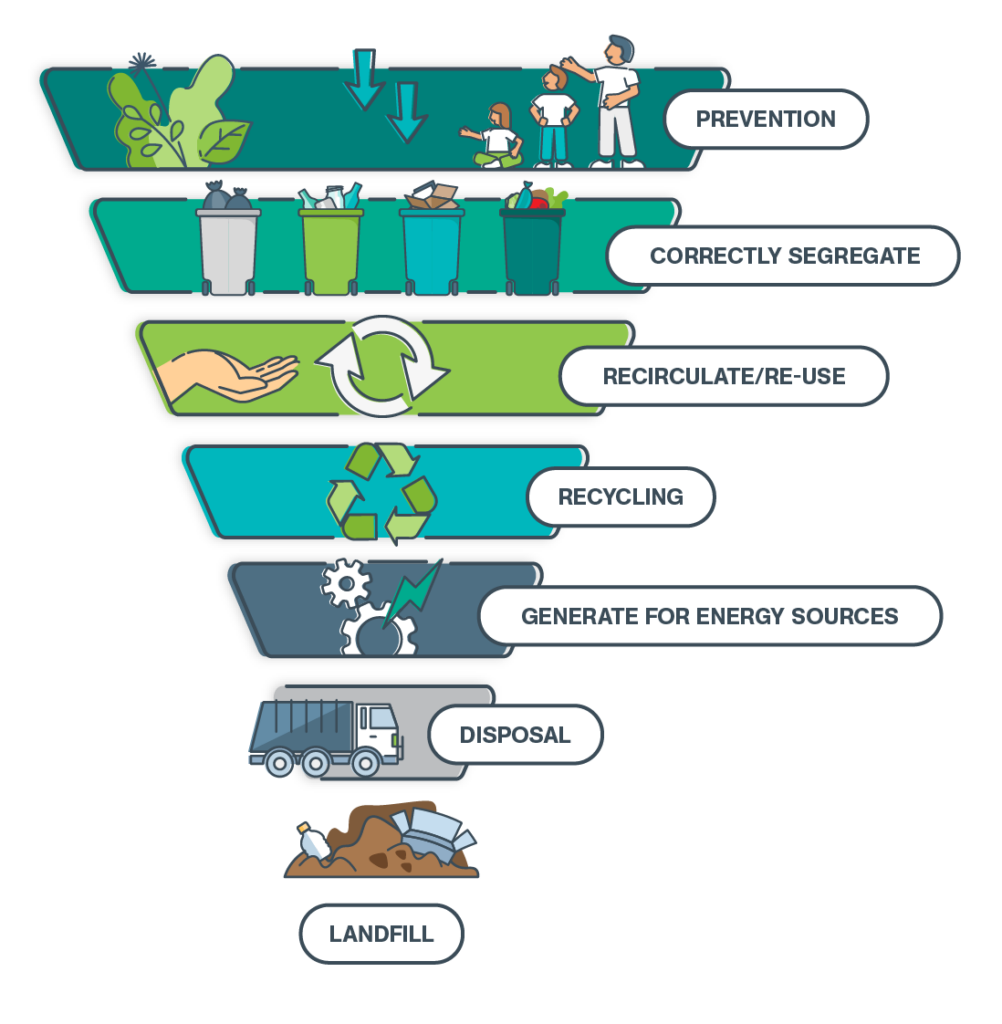
Why Is Prevention the Top Priority of the Waste Hierarchy?
Prevention is the most desirable level of the waste management hierarchy because it addresses the root cause of waste generation – overconsumption and unnecessary production. By preventing waste from being created in the first place, we can significantly reduce our environmental impact and save precious resources.
When we prevent waste, we avoid the need for subsequent waste management processes such as reuse, recycling, energy recovery and disposal. These processes often require energy and resources, further contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental problems.
By prioritising prevention, healthcare facilities can significantly reduce their carbon footprint, save costs and contribute to a more sustainable future.
How Does the Waste Hierarchy Work?
Some things are much more interesting to explain with a metaphor, so let’s imagine you’re planning a meal…
A Kitchen Metaphor
First, you prepare your ingredients by peeling, washing, and chopping them as required. Then, you mix them together for cooking, and you enjoy the finished dish once you’re finished.
Step 1: Reduce
After you’ve eaten, you have the leftovers to deal with, including any scraps from the ingredients you prepared earlier.
The waste hierarchy is similar to the process of cleaning up after a meal. The first and most favourable step is to reduce the amount of waste generated.
In the kitchen, this may mean using all the ingredients you prepared, cooking only the exact amount of food you need, and composting any scraps from your prep.
In a healthcare setting, preferred options include reducing the amount of packaging and resources used, reducing the number of disposable items, and rethinking processes to minimise the volume of waste generated.
Step 2: Reuse
However, this isn’t always possible in the kitchen or the healthcare environment. If some waste is generated, the next step is to correctly segregate your waste to see how you can reuse it.
In the kitchen, this could mean using the leftovers for another meal; you wouldn’t want any packaging in your next meal, so segregation is key before this step. In healthcare, it might involve reusing containers, packaging, or medical supplies whenever possible.
Step 3: Recycle
If reusing the waste isn’t an option, the next step is to recycle it. As noted earlier with our kitchen analogy, this could mean composting any scraps and leftovers. In healthcare settings, recyclable materials may include paper, cardboard, glass, and certain types of plastics and packaging waste.
Step 4: Disposing of Waste
Finally, our least favourable option is that if the waste cannot be recycled, it should be disposed of safely and responsibly.
By following the waste hierarchy framework, we can minimise the amount of waste generated and ensure that what remains is managed in the most environmentally friendly way possible in both kitchen and healthcare environments.
 Why Is the Waste Management Hierarchy Important in Healthcare?
Why Is the Waste Management Hierarchy Important in Healthcare?
The waste hierarchy helps to prioritise efforts to reduce waste generation in the most environmentally sustainable way. This is especially important in the healthcare industry, where large amounts of waste are produced every day.There are several more reasons why using the waste hierarchy framework is good for your healthcare facility:
- It’s cost-effective: From an economic perspective, adopting the waste hierarchy can lead to significant cost savings for healthcare organisations. The NHS Sustainable Development Unit estimates that improved waste management could save the NHS millions of pounds annually. Healthcare facilities can reduce procurement costs, waste disposal fees, and environmental impact by focusing on waste prevention and reuse, contributing to both financial sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
- It improves sustainability: Healthcare waste has a significant impact on the environment, especially when hazardous materials or infectious waste are involved. By reducing the amount of waste generated, healthcare facilities can ensure that what remains is treated in the most sustainable way. Reusing also avoids the need for manufacturing raw materials, conserving energy, and being resource efficient.
- It protects public health: By using the most favourable waste management options according to the waste hierarchy, you’ll reduce your carbon footprint, and public health will benefit.
- It supports a circular economy: Following the waste hierarchy encourages a shift towards a circular economy, where resources are used efficiently, waste is minimised, and materials are kept in use for as long as possible.
- It encourages innovation: By prioritising waste prevention and minimisation, healthcare facilities and reputable waste management providers will be encouraged to find innovative solutions to reduce waste and improve sustainability.
With the UK healthcare industry on the route to Net Zero, it’s more important than ever to use tools such as the waste hierarchy to streamline this journey for any waste producer in your healthcare facility.
Regulatory Compliance in Healthcare Waste Management
Regulatory compliance in healthcare waste management is overseen by various public bodies at the national level, including the Environment Agency and the Care Quality Commission. Healthcare facilities must comply with specific regulations such as the Hazardous Waste Regulations 2005 and the Controlled Waste Regulations 2012. These regulations ensure that healthcare waste is properly categorised, segregated, and disposed of, minimising risks to public health and the environment.
Legal Context in Healthcare Waste Management 
The waste hierarchy in healthcare is grounded in waste legislation frameworks, including the EU Waste Framework Directive, which has been incorporated into UK law.
Healthcare facilities must adhere to these regulations to ensure proper waste management and optimal environmental outcomes.
The Environmental Protection Act 1990 and the Waste (England and Wales) Regulations 2011 provide the legal basis for implementing the waste hierarchy in the UK healthcare sector.
Steps for Implementing the Waste Hierarchy
To successfully implement the waste hierarchy, you’ll need to take a holistic approach that involves every facet and moving part of your facility; from Porters, Waste Managers, Estates and Facilities Managers, to Nurses, Procurement and Purchasing.
Some steps that can help you include:
- Conducting a waste audit: Conducting a waste audit can help you identify key areas where waste reduction, recirculation, and recycling can be improved.
- Developing a waste management plan: This can help ensure the waste hierarchy is being implemented effectively and sustainably.
- Engaging staff and patients: Encourage staff and patients to reduce waste and promote sustainability. This can also help build support around sustainable waste management.
- Procuring sustainable products: Encouraging sustainable purchasing decisions and choosing reusable items over disposable ones where possible can help to reduce the amount of waste generated.
Waste Hierarchy UK | Do You Need Guidance on Your Waste Management Strategy?
Implementing a framework like the waste hierarchy into your facility’s waste management systems is a highly effective way to reduce the environmental impact of the healthcare waste your facility generates.
If your facility needs guidance when making decisions on waste management, our expert waste consultants can help you implement the waste hierarchy, conduct a waste audit of your site and waste management practices, develop a waste management plan, and provide education and training to stakeholders.
We’re dedicated to driving value in sustainability and exceeding benchmarks for the management of waste, supporting our partners on the route to net zero. To learn more about reducing your carbon footprint with waste management, contact us today.
Let's Talk!
Your time is valuable, and we don’t want to play hard to get. You can either phone us directly on the details listed on our contact page, or feel free to fill out this short form and one of our team members will get back to you as quickly as possible.
